AF-C vs AF-S: Learning The Different Auto Focus Modes
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The different types of photography require different modes and settings in a camera to bring out the best possible image for the frame. Focus mode, Aperture, Exposure, ISO etc are settings that are changed according to the needs of a photographer.
Auto Focus mode is one of these settings that apply different autofocus techniques that determines how the subject is brought into focus range. Depending on the subject’s motion they are changed so that the photo does not become blurry beyond repair.
In this article, I’ll be talking about when to use af-c vs af-s during the daily photography needs of a user.
The Different Auto Focus Modes
There are quite a few Auto Focus modes available on modern-day cameras. The most fundamental and popular modes are:
- AF-S (Single)
- AF-C (Continuous)
- AF-A (Auto)
Nikon, Canon and Sony have different terms for the focus modes but they’re all essentially the same. Here is an image that will give a general idea of the names of the focus methods on different cameras.
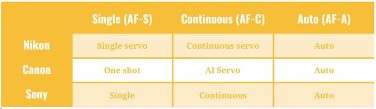
In this article, I’ll only be covering the AF-Single and the AF-Continuous and their different usage scenarios like when to use which mode of Auto Focus.
What is AF-C?
Also known as Continuous Auto Focus. In this mode, the camera focuses continuously to adjust the focus based on the subject while the shutter button is pressed and held halfway down.
This mode is mostly used to shoot subjects that are in motion. Sports photography, Nature photography or Railway photography are the prime use cases.
What is AF-S?
In this mode pressing the shutter button halfway down locks, the focus on the subject and the focus distance is also locked until the shutter is released or a photo is taken. It is also called Single-Shot Auto Focus.
The most suitable use for this mode is shooting stationary subjects, that are still. Portraits, Landscapes or general snapshots are taken using this mode.
AF-C vs AF-S: The Complete Comparison
To have a better understanding, the knowledge of what the different autofocus modes stand for is crucial.
Autofocus modes have improved substantially in the last few years. Manufacturers have implemented new technologies for cameras so that they can track faster, have more accurate focus etc.
Auto Focus Area
The area on the frame that is used by the camera to select the focus points is the autofocus area. It gives photographers a range as to where the camera will likely focus on.
The viewfinder or the integrated display shows the focus points that the camera will use for its autofocus system.
A photographer can select different points in the frame to make sure the subject is in focus and the whole image is not blurry. The autofocus modes come into play in selecting the focus area.
When using the Single-shot autofocus, the photographer selects the subject inside the frame as the main focal point since the subject is stationary. Using a Continuous autofocus system will make the camera work harder than it has to.
While shooting subjects in motion it is up to the camera to decide the focus point and photos are taken when the subject is in focus. Sports photography, for example, has lots of moving subjects and using single-shot autofocus will result in blurry images of the subject.
Taking shots
The AF-S requires the camera to lock the focus onto the subjects or pressing the shutter will not take a photo. This is due to the focus error and the mechanism behind the single-shot autofocus mode.
The AF-C or Continuous autofocus mode allows users to take photos even if the subject is not in focus which comes in handy due to the small amount of time allowed for the perfect shot to be taken.
The AF-C here gets the point for having more versatility.
Focus re-adjustment
The AF-C will automatically re-adjust focus if the subject or the camera is moved. Continuing to press the shutter halfway down will track the subject’s movement and adjust the focus accordingly.
The AF-S will only let a photographer adjust focus if the shutter is released and pressed halfway again and even then the subject needs to be still for it to lock and hold focus on it.
The Continuous autofocus or the AF-C gets another point here.
Control and Precision
The AF-S gives more control and precision to the users as they can utilize the abundance of focus points to precisely focus on the subject. This is true in taking landscapes, still portraits, macros or architecture photographs.
AF-C will try to re-adjust focus but if it fails then the resulting image will be blurry and the subjects out of focus. It comes down to letting the camera decide or control how and where to focus which may destroy the photo of your life.
The AF-S is the winner for offering more control over the final image.
Battery Drainage
AF-C uses a lot of battery because the camera has to constantly adjust for the movement of the subjects to keep them sharp as a tack. The camera has to work harder and that drains more battery.
AF-S however does not drain the battery as much as AF-C. The camera works to lock focus only when the shutter is pressed halfway. It also does not let users take photos if subjects are not in focus reducing redundant blurry images.
The winner here is the AF-S or Single-shot autofocus because it consumes less battery.
AF-C vs AF-S: Which one to use?
Changing the autofocus mode isn’t a big hassle either. Some cameras have a dedicated ‘AF-Mode’ button for ease of use.
However, there is an ‘Auto’ option to let the camera decide which mode to use and when. For beginners, that is a great setting to use until they understand the fundamentals of the different auto-focus modes.
But if your camera does not come with an auto selection mode then sticking with the AF-C would be the wisest choice as it can take photos of moving subjects as well as take sharp shots of still subjects.
The AF-S on the other hand won’t allow one to take photos of moving subjects as it is harder to lock and hold focus on the subject.
The AF-C mode or the Continuous autofocus mode takes the crown.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why are my DSLR pictures not sharp?
There are 3 main reasons for blurry photos.
If images are a bit blurry or out of focus then the cause may be one of the three –
Shutter speed issue.
Autofocus issue.
Depth of field issue.
Try changing the values of these or use different autofocus modes to see if the problem persists before taking the camera to be looked at.
Do professional photographers use autofocus?
They do and they don’t.
Manual focusing used to be the only method of focusing for professionals back in the day. But with modern technology and advancements in camera autofocus, some have been swayed.
But most professionals forego using autofocus because manual focus gives them more control over the images.
When should you not use autofocus?
In low light conditions.
Autofocus suffers when subjects are non-contrasting and have trouble working properly in low light conditions.
Summary
There is no clear winner as to which autofocus mode a photographer should use. Ultimately, it comes down to the subject of the photo and the type of photography a user is into.
Photographers use different modes for different subjects and scenarios. Sticking to one mode of autofocus can ruin potentially astounding photos.
I hope this article helps you utilize the different auto-focus modes and capture stunning photographs.
- Read Also: Exposure: Overexpose or Underexpose? A Detailed Guide
- Read Also: Denoise or Sharpen First to Adjust the Color and Luminosity?
- Read Also: 24p 100m vs 24p 60m: What Is The Importance Of Choosing The Right Bitrate For Video?
- Read Also: AI Focus vs AI Servo: Which is Best?
- Read Also: Long GOP vs All Intra: What is the Difference?



